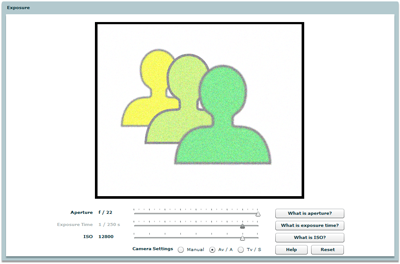
Exposure
Lens Applets
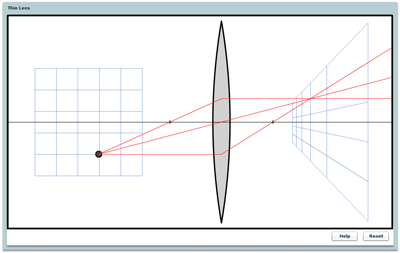
Thin Lens
Uses Gauss's ray tracing construction to show how thin lenses perform a 3D perspective transformation of object space into image space.
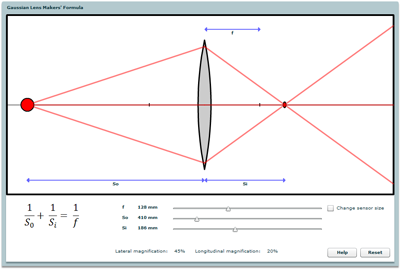
The Gaussian Lens-Maker's Formula
The relationship between object distance, image distance, and focal length, and the distinction between focusing and zooming.
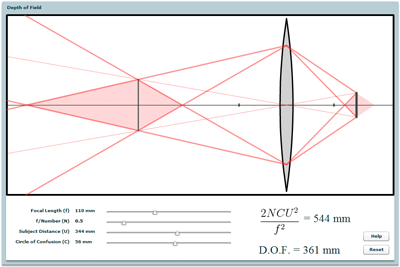
Depth of Field
How do focal length, subject distance, F-number, and size of the circle of confusion affect depth of field?Telephoto Zoom Lens
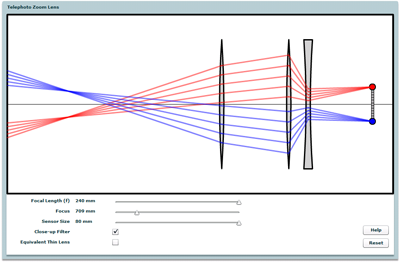
The operation of zoom lenses, telephoto zoom lenses, and optically-compensated telephoto zoom lens.
Convolution
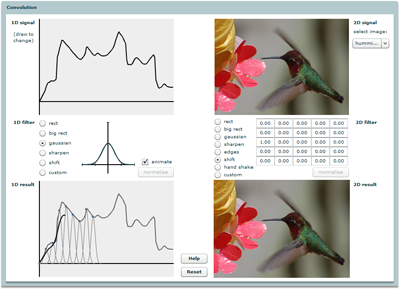
Spatial convolution
Interactively demonstrates 1D continuous convolution and 2D discrete convolution. Don't miss the "custom" buttons!
Autofocus
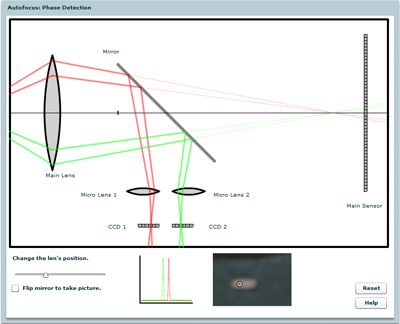
Autofocus: Phase Detection
Explore how some cameras (mostly SLRs) use phase detection to autofocus a picture.
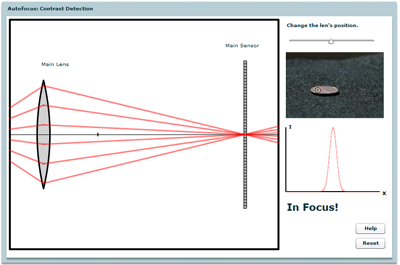
Autofocus: Contrast Detection
Explore how other cameras (mostly point-and-shoots) use contrast detection to autofocus an image.
Color
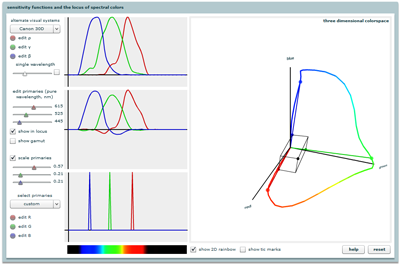
Introduction to Color Theory
Explores the trichromatic theory of color vision and considers its implications for human perception, color photography, and computer display of color images.
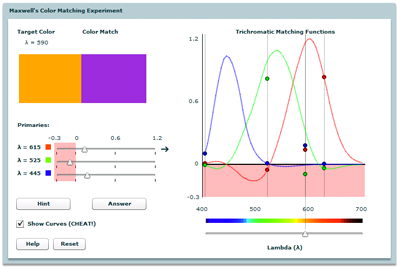
Color Matching
Reenact Maxwell's color matching experiment to see how closely you can match the trichromatic matching functions for the given primaries.
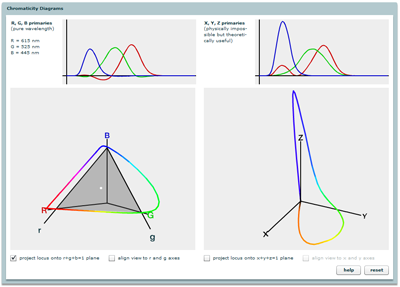
Chromaticity Diagrams
Explores chromaticity diagrams and the meaning of the 2D gamut of perceivable colors.
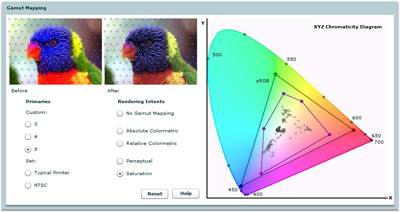
Gamut Mapping
Interactively shows the results of gamut mapping (both the primaries and the rendering intents) on the colors displayed in an image.
Color Mixing
Explores additive and subtractive color mixing.Gamma
Gamma Correction
Unwrapping some of the tangled world of gamma correction.Panoramas
Cylindrical Panoramas
Demonstrates how images are projected from a plane to a cylinder to form a panorama.